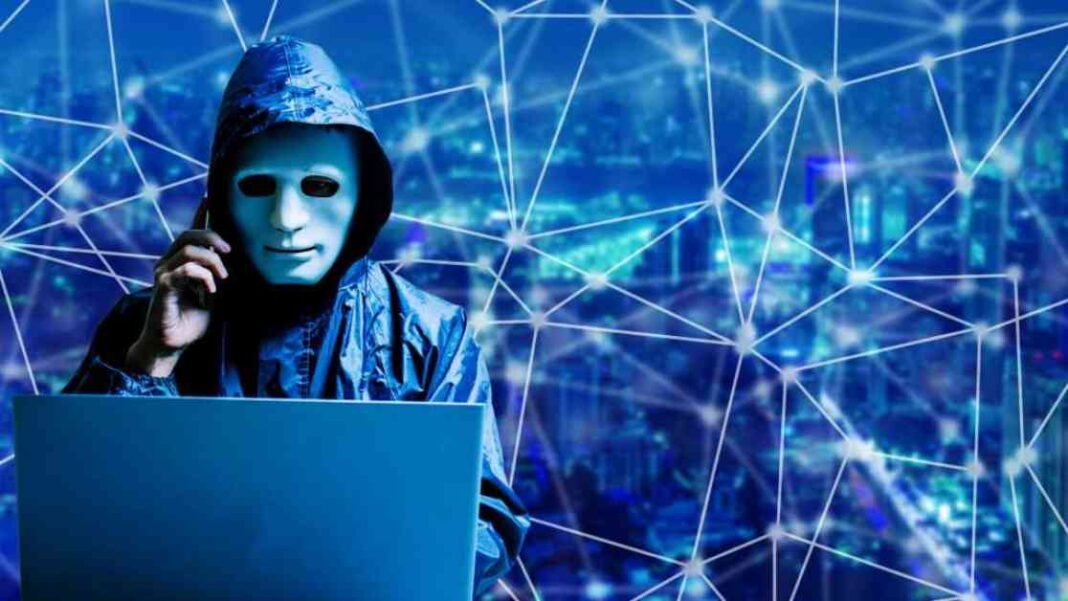
The internet that we see and use through web browsers like Edge, Chrome, Firefox, Opera, and Safari only scratches the surface of what is truly out there. There exists a hidden side of the web called the darknet, where information can be shared and exchanged with utmost anonymity. Initially noted by PCWorld in 2013, the darknet serves as a platform for freedom of information in countries with strict censorship laws, but it also attracts a significant number of criminals.
Darknet marketplaces offer a wide range of illegal products and services, including drugs, counterfeit money, weapons, and stolen data like credit card information. Due to the misuse of these items for criminal activities, the darknet has garnered increased public attention over the years. Users of the darknet strive to remain unidentified at any cost to evade law enforcement.
The darknet, as its name suggests, is a network primarily used for anonymous communication on the internet. Anonymization services within the darknet prevent surveillance of online activities. The Tor network, in particular, is highly favored for maintaining anonymity. Tor, short for “The Onion Router,” operates by routing data packets through various random nodes before reaching the open internet through an exit node. This process involves multiple layers of encryption, making it difficult for eavesdroppers to intercept the data.
Tor not only ensures secure browsing but also hosts hidden websites on Tor servers that are inaccessible through the regular internet. These hidden websites have addresses with the *.onion extension, and they are only visible to specific nodes within the Tor network. Various directories and search tools like the Hidden Wiki, Torch, Ahmia, and Haystack facilitate access to these hidden services.
When users click on an encrypted *.onion link, the request passes through several computers before reaching a connection node that knows the real address of the server. This method of routing data prevents the exact location of the server from being traced. Payment for services on the darknet is commonly made using Bitcoins for maximum anonymity.
To access the darknet, users often employ the Tor browser, which can be installed in a virtual machine to minimize traceable actions. Specialized darknet search engines like Torch, Ahmia, and Haystack, or directories like the Hidden Wiki, are necessary tools for navigating the darknet as traditional search engines do not work within this network.
The Tor Browser itself is a legal tool that can be used for anonymous internet surfing without engaging in illegal activities. By following simple steps to connect to Tor, users can ensure their anonymity online. The slower loading times experienced while using the Tor Browser are a result of the anonymization process that routes data packets through multiple nodes.
In conclusion, the darknet presents a secretive underworld on the web where users can operate anonymously and access a variety of illicit goods and services. By understanding the workings of the darknet and utilizing tools like the Tor network, individuals can explore this hidden realm while maintaining their privacy.