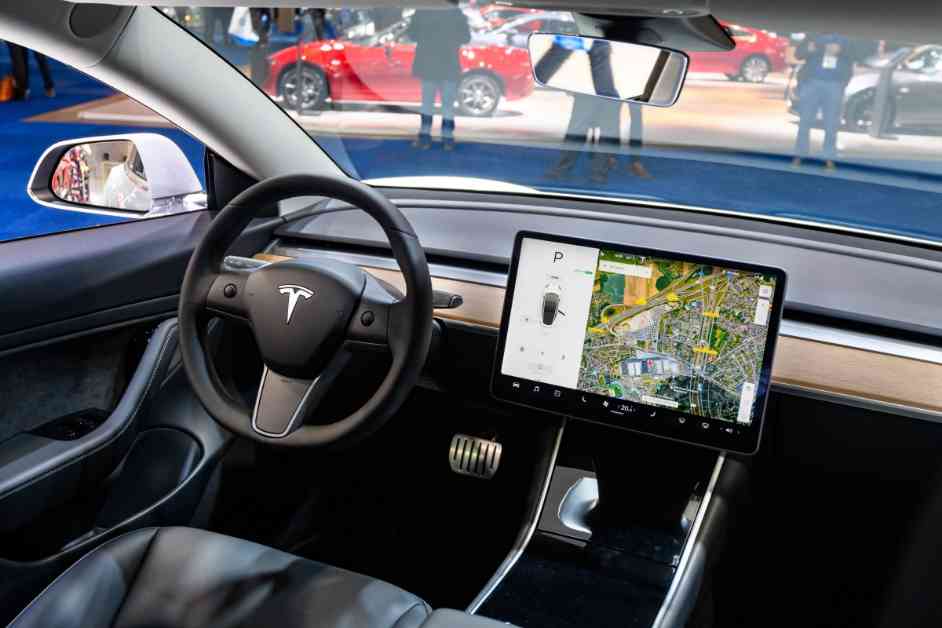
The National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) has launched an investigation into Tesla’s Full Self-Driving (Supervised) software following four reported crashes in low-visibility conditions, one of which resulted in a pedestrian fatality. The agency is looking into whether the software can effectively detect and respond to reduced roadway visibility due to factors like sun glare, fog, or airborne dust. Additionally, NHTSA aims to determine if there have been other unreported crashes in similar conditions.
This investigation comes shortly after Tesla CEO Elon Musk unveiled the prototype of the “CyberCab,” a two-seater car intended to operate as a robotaxi. Musk also mentioned plans for Tesla’s Model 3 sedan and Model Y SUV to achieve unsupervised operation in California and Texas by 2025, although specifics on how this will be achieved were not provided.
In the past, NHTSA concluded a nearly three-year investigation into Tesla’s Autopilot system, which resulted in 13 fatal crashes out of nearly 500 incidents involving the software. Concurrently, a new investigation was opened to assess the effectiveness of the recall fix implemented by Tesla to address Autopilot issues.
Beyond regulatory scrutiny, Tesla is facing legal challenges regarding its driver-assistance features. The Department of Justice is investigating the company’s claims, while the California Department of Motor Vehicles has accused Tesla of overstating the capabilities of its software. Tesla has settled some lawsuits related to Autopilot crashes and maintains that drivers are responsible for monitoring the system and intervening when necessary.
The latest investigation by NHTSA focuses on four crashes involving Tesla’s Full Self-Driving (Supervised) software between November 2023 and May 2024. These incidents occurred in various locations under challenging weather conditions, resulting in fatalities and injuries.
NHTSA’s defects investigations undergo several stages, with the current probe categorized as a preliminary evaluation. Typically, the agency aims to complete such investigations within eight months to determine any potential safety concerns related to the technology.
As the investigation progresses, more information from NHTSA’s filings will shed light on the circumstances surrounding the crashes and the performance of Tesla’s Full Self-Driving (Supervised) software. Stay tuned for updates on this developing story.