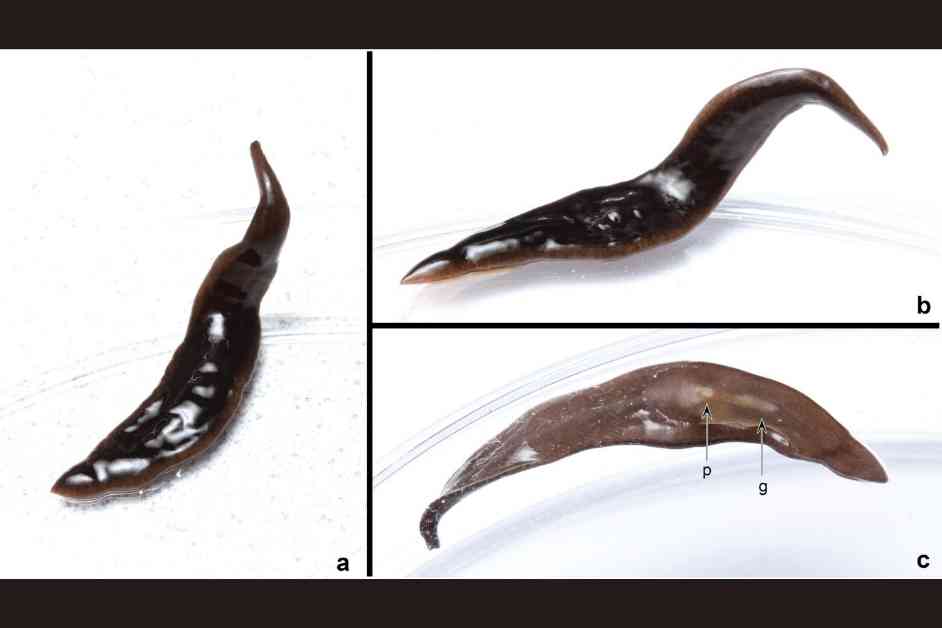
The United States is facing a new threat in the form of an invasive flatworm species. Scientists have recently discovered a previously unknown type of flatworm in several states, including North Carolina, Georgia, and Florida. This predatory worm, named Amaga pseudobama, is believed to have originated from South America and is closely related to other invasive species, making it challenging to track its presence in the U.S.
Unlike native species, invasive species like A. pseudobama can disrupt ecosystems by outcompeting native animals for resources or habitat. However, much remains unknown about these newly discovered worms. According to Matt Bertone from North Carolina State University, researchers have not observed the worm in its native habitat, making it difficult to determine its impact on the environment.
An international team of researchers from France, Australia, Poland, and the U.S. collaborated to identify the mystery worm. Initially thought to be Obama nungara, a species from South America invading Europe, further analysis revealed that it was a new species of the genus Amaga. Despite its resemblance to O. nungara, the researchers decided to name the new worm A. pseudobama due to its similarities.
While some flatworms are parasites, land flatworms like O. nungara and A. pseudobama are predators, feeding on earthworms, snails, and other invertebrates. It is suspected that A. pseudobama originated in South America and has likely spread across the U.S., including states like Florida, Georgia, and potentially Texas and California.
Studying the impact of A. pseudobama on native ecosystems is crucial, but its resemblance to other flatworm species complicates this task. Researchers believe that further research is needed to understand the potential risks posed by these invasive worms and their effects on native wildlife.
In conclusion, the discovery of A. pseudobama highlights the importance of studying and identifying new species to protect ecosystems from invasive threats. While these flatworms may seem insignificant, their impact on the environment could be significant, underscoring the need for ongoing research and conservation efforts.